原计划一周一个模块,但是看到 runTime 这里持续时间有点长,底层内容很多啊,原因还是之前基础太差,菜的抠脚。。。还有整理完 block 后再想 block hook 应该怎么实现,瞎搞了一通最后找到了开源的库 blockHook,看了几天的源码发现底层掌握的还是不牢,其中包括 runtime 部分,先整理完 runtime 部分然后再回头重新分析 blockHook。
下文内容是根据 objc4-723 版本分析的,目前最新版本是 objc4-781 ,最新版本做了一些优化,不过不影响我们理解。
isa 详解 在 arm64 结构之前,isa 就是一个普通指针,存储着 Class、Meta-Class 对象的内存地址。
从 arm64 结构开始,对 isa 进行了优化,变成了一个共用体(union)结构,使用位域来存储更多信息
更多信息是指 isa 除了存储对象内存地址外还存储了其他的信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 union isa_t { Class cls; uintptr_t bits; # if __arm64__ # define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL # define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x000003f000000001ULL # define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x000001a000000001ULL struct { uintptr_t nonpointer : 1; uintptr_t has_assoc : 1; uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1; uintptr_t shiftcls : 33; uintptr_t magic : 6; uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1; uintptr_t deallocating : 1; uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1; uintptr_t extra_rc : 19; }; };
nonpointer:0 代表普通指针,存储着 Class、Meta-Class 对象的内存地址,1 代表优化过,使用位域存储更对信息
has_assoc:是否有设置过关联对象,如果没有释放时更快
has_cxx_dtor:是否有 C++ 的析构函数(.cxx_destruct),如果没有释放时更快
shiftcls:存储着 Class、Meta-Class 对象的内存地址信息
magic:用于在调试时分辨对相关是否完成初始化
weakly_referenced:是否有被弱引用指向过,如果没有,释放更快
deallocating: 对象是否正在释放
has_sidetable_rc:引用计数器是否过大无法存储在isa中。1标识引用计数会存储在side table的类属性中
extra_rc:里面存储的值是引用计数器减1
这里可以简单看一下实例对象 isa 指针里面存储的类,我们这里只研究 arm64 架构,可以看到上面有 ISA_MASK,这个是用来取 Class、Meta-Class 对象的内存地址的,来个小实验:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 NSLog(@"--- %p" , [ViewController class ]); 结果: --- 0x1000b1cf0 再来打印 self 的 isa: (lldb) p/x self ->isa (Class) $0 = 0x000005a1000b1cf7 ViewController 可以看到上面的两个地址是不一样的,根据上面的结构,我们使用 ISA_MASK 来取一下 isa 中关于对象的内存地址: (lldb) p/x 0x000005a1000b1cf7 & 0x0000000ffffffff8 ULL (unsigned long long) $1 = 0x00000001000b1cf0 由上可以看到,由 isa 取出来的地址和 ViewController class 类的真实地址是一样的。
关于上述标记位中更快释放,可以再 objc4 里面看到源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 inline void objc_object::rootDealloc() { if (isTaggedPointer()) return; // fixme necessary? if (fastpath(isa.nonpointer && !isa.weakly_referenced && !isa.has_assoc && !isa.has_cxx_dtor && !isa.has_sidetable_rc)) { assert(!sidetable_present()); free(this); } else { object_dispose((id)this); } } id object_dispose(id obj) { if (!obj) return nil; objc_destructInstance(obj); free(obj); return nil; } void *objc_destructInstance(id obj) { if (obj) { // Read all of the flags at once for performance. bool cxx = obj->hasCxxDtor(); bool assoc = obj->hasAssociatedObjects(); // This order is important. if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj); if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj); obj->clearDeallocating(); } return obj; }
如上,在 dealloc 时会分别获取是否有关联对象、析构函数、弱指针等标记位,如果没有是直接释放的,否则会调用相关的方式释放对应的资源。
Class 结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 struct objc_object { Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY; }; struct objc_class : objc_object { // Class ISA; Class superclass; cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags } bits & FAST_DATA_MASK 可以拿到 class_rw_t struct class_rw_t { uint32_t flags; uint32_t version; const class_ro_t *ro; method_array_t methods; property_array_t properties; protocol_array_t protocols; Class firstSubclass; Class nextSiblingClass; char *demangledName; } struct class_ro_t { uint32_t flags; uint32_t instanceStart; uint32_t instanceSize; #ifdef __LP64__ uint32_t reserved; #endif const uint8_t * ivarLayout; const char * name; method_list_t * baseMethodList; protocol_list_t * baseProtocols; const ivar_list_t * ivars; const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout; property_list_t *baseProperties; };
class_rw_t 里面的 methods、properties、protocols 是二维数组,是可读可写的,包含类的初始内容、分类的内容。
1 2 3 4 5 class method_array_t : public list_array_tt<method_t , method_list_t > { typedef list_array_tt<method_t , method_list_t > Super; };
Class_ro_t 里面的 baseMethodList、baseProtocols、ivars、baseProperties 是一维数组,是只读的,包含了类的初始信息。
下面来看下 method_t 的结构:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 struct method_t { SEL name; // 函数名 const char *types; // 编码(返回值类型、参数类型) IMP imp; // 指向函数的指针(函数地址) struct SortBySELAddress : public std::binary_function<const method_t&, const method_t&, bool> { bool operator() (const method_t& lhs, const method_t& rhs) { return lhs.name < rhs.name; } }; };
IMP 代表函数的具体实现:
typedef id _Nullable (*IMP)(id _Nonnull, SEL _Nonnull, ...);
SEL 代表方法\函数名,一般称作选择器,底层结构和 char* 类型
可以通过 @selector() 和 sel_registerName() 获得
可以通过 sel_getName() 和 NSStringFromSelector() 转成字符串
不同类中相同名字的方法,所对应的方法选择器是相同的
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
types 是包含了函数返回值、参数编码的字符串
方法缓存 Class 内部结构用有个方法缓存(cache_t),用散列表(哈希表)来缓存曾经调用过的方法,可以提高方法的查找速度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 struct bucket_t { private: cache_key_t _key; // SEL 作为 key IMP _imp; // 函数的内存地址 public: inline cache_key_t key() const { return _key; } inline IMP imp() const { return (IMP)_imp; } inline void setKey(cache_key_t newKey) { _key = newKey; } inline void setImp(IMP newImp) { _imp = newImp; } void set(cache_key_t newKey, IMP newImp); }; struct cache_t { struct bucket_t *_buckets; // 散列表 mask_t _mask; // 散列表长度 - 1 mask_t _occupied; // 已经缓存的方法数量 public: struct bucket_t *buckets(); mask_t mask(); mask_t occupied(); void incrementOccupied(); void setBucketsAndMask(struct bucket_t *newBuckets, mask_t newMask); void initializeToEmpty(); mask_t capacity(); bool isConstantEmptyCache(); bool canBeFreed(); static size_t bytesForCapacity(uint32_t cap); static struct bucket_t * endMarker(struct bucket_t *b, uint32_t cap); void expand(); void reallocate(mask_t oldCapacity, mask_t newCapacity); struct bucket_t * find(cache_key_t key, id receiver); static void bad_cache(id receiver, SEL sel, Class isa) __attribute__((noreturn)); };
再来看下获取 cache 的实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 // 如果 i为0则从mask开始查找(mask为表长度-1),如果i不为空则从i-1开始查找 static inline mask_t cache_next(mask_t i, mask_t mask) { return i ? i-1 : mask; } bucket_t * cache_t::find(cache_key_t k, id receiver) { assert(k != 0); bucket_t *b = buckets(); mask_t m = mask(); mask_t begin = cache_hash(k, m); mask_t i = begin; do { if (b[i].key() == 0 || b[i].key() == k) { return &b[i]; } } while ((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin); // hack Class cls = (Class)((uintptr_t)this - offsetof(objc_class, cache)); cache_t::bad_cache(receiver, (SEL)k, cls); }
散列表扩容,从源码可以看到,每次扩容都是原来容积的两倍,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void cache_t::expand() { cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked(); uint32_t oldCapacity = capacity(); uint32_t newCapacity = oldCapacity ? oldCapacity*2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE; if ((uint32_t)(mask_t)newCapacity != newCapacity) { // mask overflow - can't grow further // fixme this wastes one bit of mask newCapacity = oldCapacity; } reallocate(oldCapacity, newCapacity); }
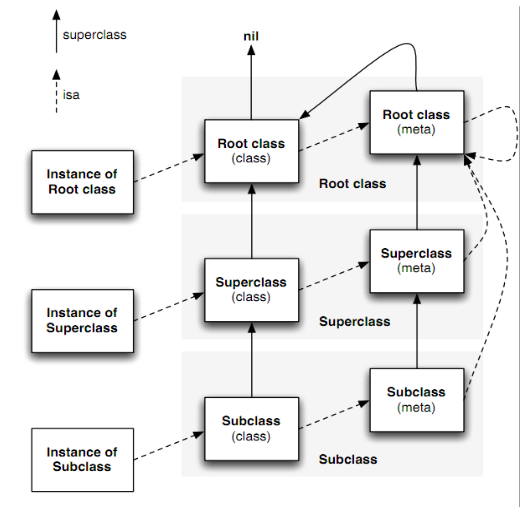
objc_msgSend 执行流程 第一个阶段 - 消息发送 看一下下面的经典调用图片
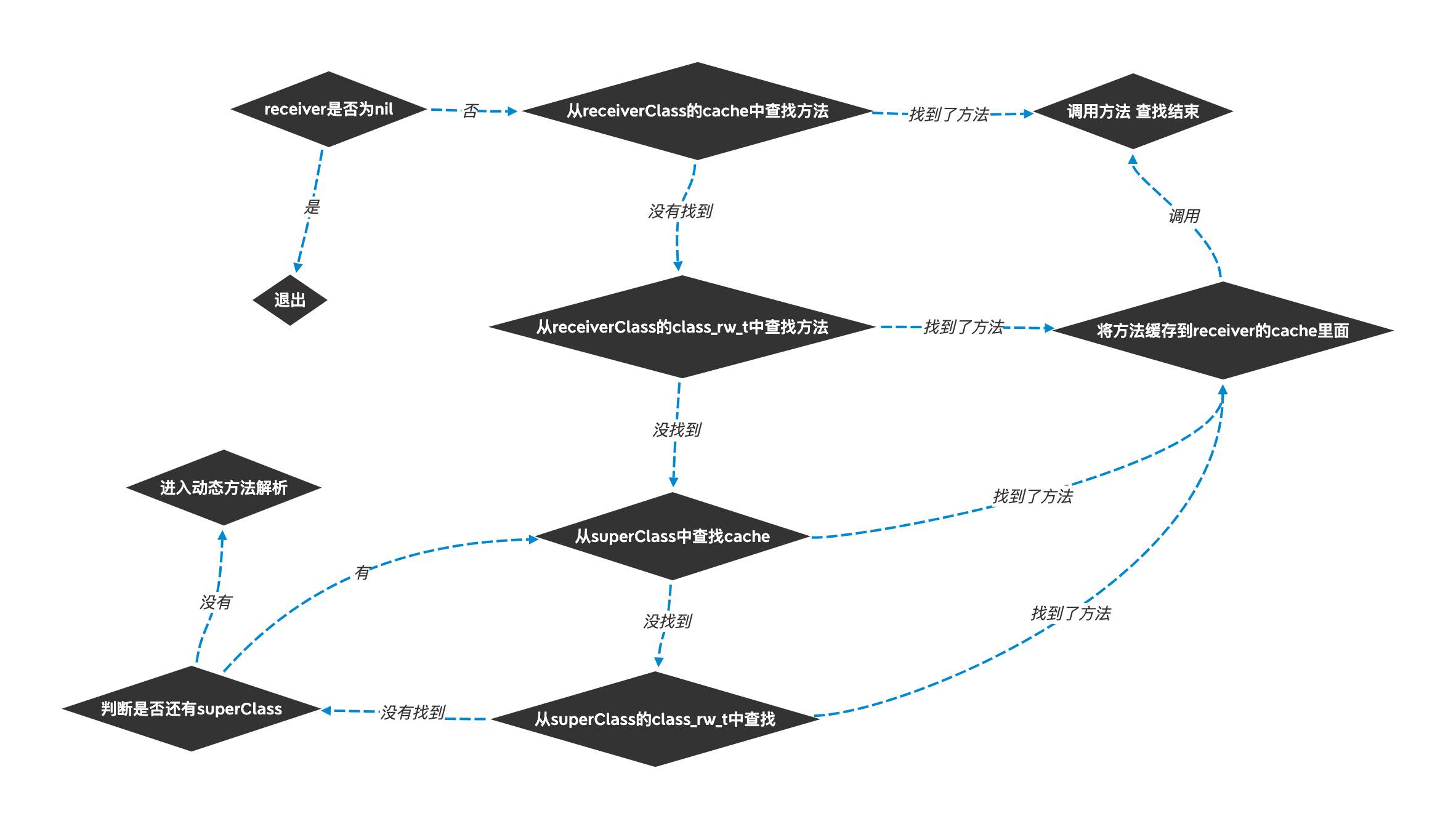
下面看下消息发送的流程:
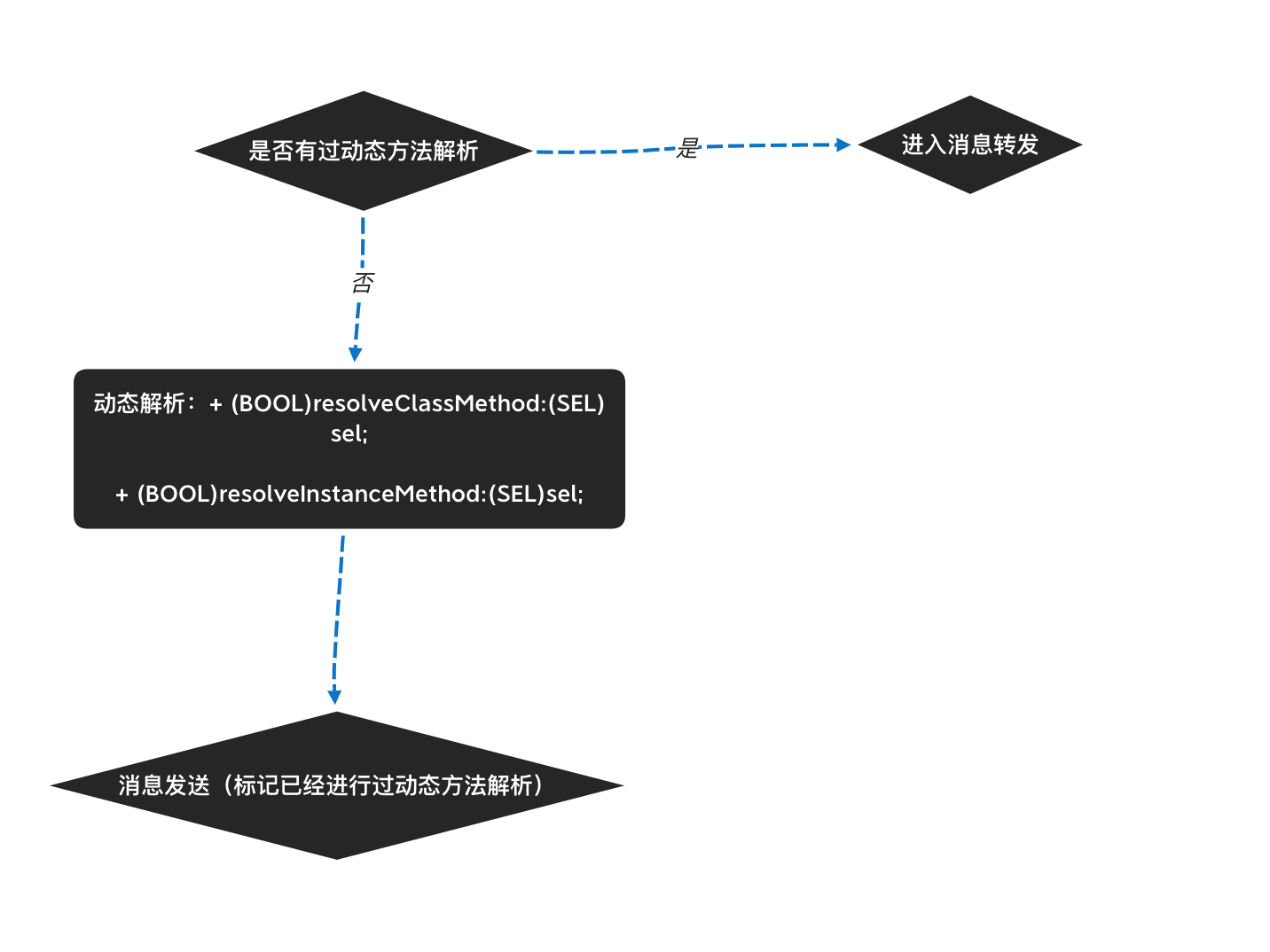
第二个阶段 - 动态方法解析 调用流程如下:
这里可以从 objc 的源码里面查到(lookUpImpOrForward 方法):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 if (resolver && !triedResolver) { runtimeLock.unlockRead(); _class_resolveMethod(cls , sel, inst); runtimeLock.read(); triedResolver = YES; goto retry; } imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache; cache_fill(cls , sel, imp, inst);
可以看到标记位 triedResolver 和我们流程图里面对应。
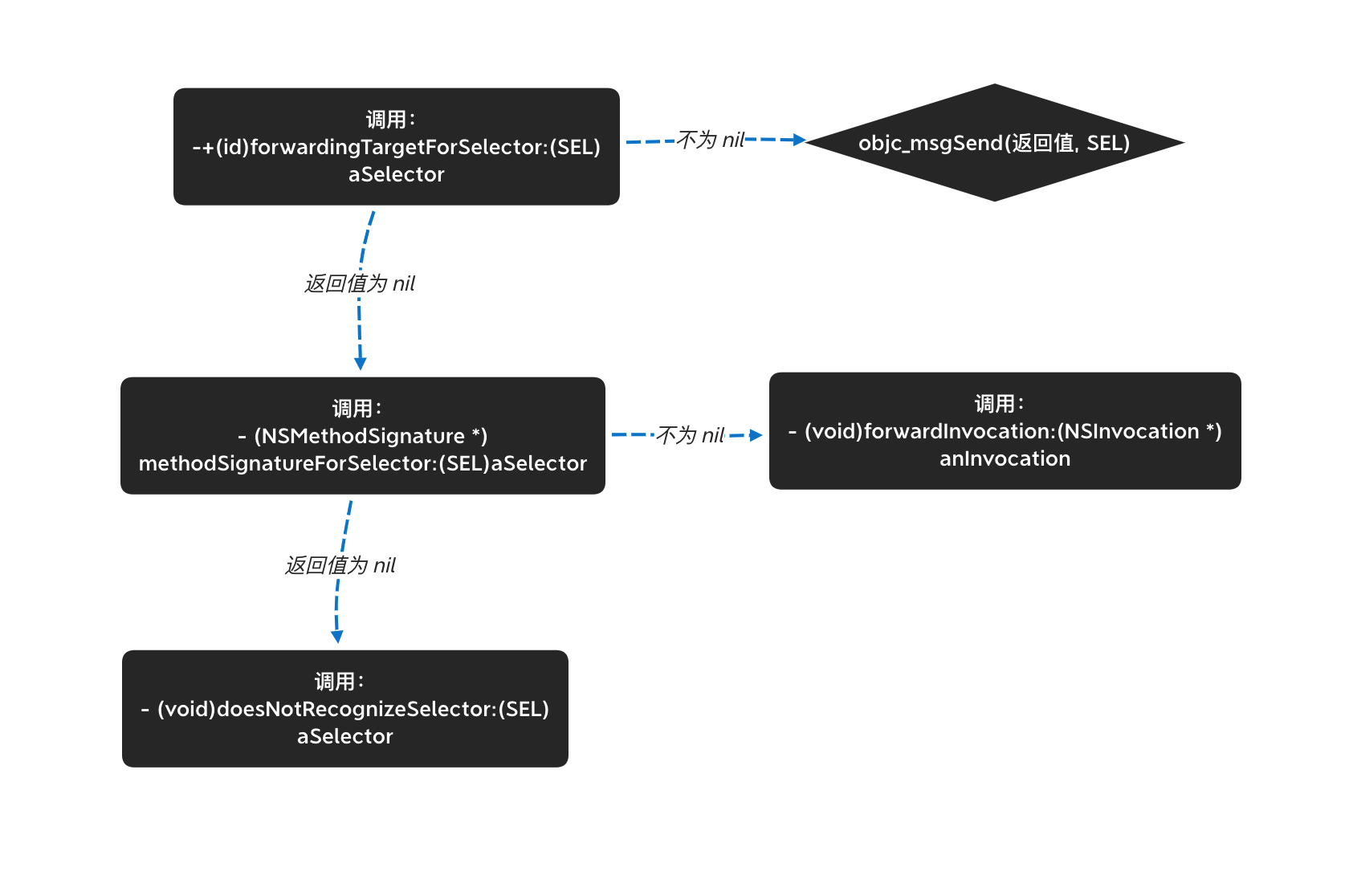
第三个阶段 - 消息转发 看下流程图:
由于消息转发阶段没有开源,这里在网上扒出大神整理的伪代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 int __forwarding__(void *frameStackPointer, int isStret) { id receiver = *(id *)frameStackPointer; SEL sel = *(SEL *)(frameStackPointer + 8 ); const char *selName = sel_getName(sel); Class receiverClass = object_getClass(receiver); if (class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass, @selector (forwardingTargetForSelector:))) { id forwardingTarget = [receiver forwardingTargetForSelector:sel]; if (forwardingTarget && forwardingTarget != receiver) { if (isStret == 1 ) { int ret; objc_msgSend_stret(&ret,forwardingTarget, sel, ...); return ret; } return objc_msgSend(forwardingTarget, sel, ...); } } const char *className = class_getName(receiverClass); const char *zombiePrefix = "_NSZombie_" ; size_t prefixLen = strlen(zombiePrefix); if (strncmp(className, zombiePrefix, prefixLen) == 0 ) { CFLog (kCFLogLevelError, @"*** -[%s %s]: message sent to deallocated instance %p" , className + prefixLen, selName, receiver); <breakpoint-interrupt> } if (class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass, @selector (methodSignatureForSelector:))) { NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [receiver methodSignatureForSelector:sel]; if (methodSignature) { BOOL signatureIsStret = [methodSignature _frameDescriptor]->returnArgInfo.flags.isStruct; if (signatureIsStret != isStret) { CFLog (kCFLogLevelWarning , @"*** NSForwarding: warning: method signature and compiler disagree on struct-return-edness of '%s'. Signature thinks it does%s return a struct, and compiler thinks it does%s." , selName, signatureIsStret ? "" : not, isStret ? "" : not); } if (class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass, @selector (forwardInvocation:))) { NSInvocation *invocation = [NSInvocation _invocationWithMethodSignature:methodSignature frame:frameStackPointer]; [receiver forwardInvocation:invocation]; void *returnValue = NULL ; [invocation getReturnValue:&value]; return returnValue; } else { CFLog (kCFLogLevelWarning , @"*** NSForwarding: warning: object %p of class '%s' does not implement forwardInvocation: -- dropping message" , receiver, className); return 0 ; } } } SEL *registeredSel = sel_getUid(selName); if (sel != registeredSel) { CFLog (kCFLogLevelWarning , @"*** NSForwarding: warning: selector (%p) for message '%s' does not match selector known to Objective C runtime (%p)-- abort" , sel, selName, registeredSel); } else if (class_respondsToSelector(receiverClass,@selector (doesNotRecognizeSelector:))) { [receiver doesNotRecognizeSelector:sel]; } else { CFLog (kCFLogLevelWarning , @"*** NSForwarding: warning: object %p of class '%s' does not implement doesNotRecognizeSelector: -- abort" , receiver, className); } kill(getpid(), 9 ); }
Super 本质 super 本质调用 了解完 objc_msgSend 机制再来看下 super 的本质。
做个测试,重写 forwardInvocation 方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 - (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation { [super forwardInvocation:anInvocation]; } 使用 clang 查看转换成的 c++ 代码 ((void (*)(__rw_objc_super *, SEL, NSInvocation *))(void *)objc_msgSendSuper)((__rw_objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("MJPerson"))}, sel_registerName("forwardInvocation:"), (NSInvocation *)anInvocation); 删除强制转换: objc_msgSendSuper( {self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("MJPerson"))}, sel_registerName("forwardInvocation:"), anInvocation);
如上,使用 super 调用方法的时候不再是 objc_msgSend,而是 objc_msgSendSuper,发送消息时有三个参数:
结构体 struct __rw_objc_super
方法名 SEL
参数 anInvocation
这里主要看下第一个参数:
1 2 3 4 5 struct __rw_objc_super struct objc_object struct objc_object __rw_objc_super(struct objc_object struct objc_object };
根据上面 objc_msgSendSuper 初始化的调用可以看到,super 的实质其实还是向 self 发送消息,receiver 依然是 self,只不过第二个参数是 superClass。
所以 super 的本质就是向 self(receiver)发送消息,不过查找方法时是从 super 开始查找。
其实这里看到的也并非最终的调用方式,通过源码或者汇编代码,或者用 这里 调试查看,最终 super 生成的结构是:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 struct objc_super2 { id receiver Class current_class } ENTRY _objc_msgSendSuper2ldr r9 , [r0 , #CLASS ] // class = struct super->class// 通过 current_class 找到 superClass ldr r9 , [r9 , #SUPERCLASS ] // class = class->superclassCacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSendSuper2// cache hit, IMP in r12 , eq already set for nonstret forwarding ldr r0 , [r0 , #RECEIVER ] // load real receiverbx r12 // call impCacheLookup2 NORMAL, _objc_msgSendSuper2// cache miss ldr r9 , [r0 , #CLASS ] // class = struct super->classldr r9 , [r9 , #SUPERCLASS ] // class = class->superclassldr r0 , [r0 , #RECEIVER ] // load real receiverb __objc_msgSend_uncachedEND_ENTRY _objc_msgSendSuper2
不管是 objc_super 还是 objc_super2,对这里的理解是没有影响的,消息的接收者就是 self,不过查找方法是从 superClass 开始查找的。
结合消息发送机制对 super 调用方法的疑问
昨天写到 super 的时候突然想到了一个问题,就是 super 的本质是:消息接受者为 self,不过查找方法是在 superClass 开始查找,根据消息发送机制,查找到方法后会将 IMP 存入到 bucket 里面。
注意:这里的 bucket 是哪个 cls 的呢?
由于对上面 【4、消息发送】那张经典图片理解的不够,认为查找到目标方法后就是把对应的方法放到 receiver 的 cache_t 里面,结果就有了下面的这个猜想。。。
猜想是这样的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @interface Student : NSObject - (void)studentTest; @end @implementation Student - (void)studentTest { NSLog(@"%s", __func__); } @end @interface GoodStudent : Student - (void)test; @end @implementation GoodStudent - (void)studentTest { [super studentTest]; NSLog(@"%s", __func__); } - (void)test { [super studentTest]; [self studentTest]; } @end
如上我们使用 GoodStudent 实例调用 test 方法,
当调用完 [super studentTest];后,GoodStudent 的 cache_t 里面就应该有了studentTest方法的缓存
当执行 [self studentTest];时,根据消息发送机制,在缓存中查找到了第一步调用的缓存,也就是 superClass 的方法缓存
所以结果就是只要缓存还在就不会调用到 self 的 studentTest 方法
看完我的猜想是不是感觉很扯,但是就这困惑了我很久,从昨天晚上开始查资料,一直到今天早上早早来公司,看了半天 objc 的源码才找到答案,其实答案已经看过很多遍,不过由于根据网络上面各种文章的洗脑,从来没有静下心来一句一句的分析 objc 的源码,现在来看下这个很扯的想法是怎样被推翻的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 // 1、执行 [super studentTest]; // 2、会调用 lookUpImpOrForward 方法,注意:inst 就是 receiver(self),cls 就是 superClass IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior) // 3、查找到方法后会调用 log_and_fill_cache,这里 receiver 就是 self,cls 为 superClass static void log_and_fill_cache(Class cls, IMP imp, SEL sel, id receiver, Class implementer) // 4、调用 cache_fill 方法 // 看下缓存的 cache_t 是在 cls 里面取出来的,而将 imp 缓存到 cache 时会调用 cache->insert void cache_fill(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver) { if (cls->isInitialized()) { cache_t *cache = getCache(cls); cache->insert(cls, sel, imp, receiver); } } // 5、cache->insert 方法 // 注意这里 set 缓存时,是放在了 cls 里面,而 receiver 的作用就是在设置缓存失败时接收消息,这就对上了,因为self 本来就是单纯的 receiver,和方法的缓存没有关系,这里方法的缓存只和 cls 有关 void cache_t::insert(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver) { // Use the cache as-is if it is less than 3/4 full mask_t newOccupied = occupied() + 1; unsigned oldCapacity = capacity(), capacity = oldCapacity; if (slowpath(isConstantEmptyCache())) { // Cache is read-only. Replace it. if (!capacity) capacity = INIT_CACHE_SIZE; reallocate(oldCapacity, capacity, /* freeOld */false); } else if (fastpath(newOccupied <= capacity / 4 * 3)) { // Cache is less than 3/4 full. Use it as-is. } else { capacity = capacity ? capacity * 2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE; if (capacity > MAX_CACHE_SIZE) { capacity = MAX_CACHE_SIZE; } reallocate(oldCapacity, capacity, true); } bucket_t *b = buckets(); mask_t m = capacity - 1; mask_t begin = cache_hash(sel, m); mask_t i = begin; // Scan for the first unused slot and insert there. // There is guaranteed to be an empty slot because the // minimum size is 4 and we resized at 3/4 full. do { if (fastpath(b[i].sel() == 0)) { incrementOccupied(); b[i].set<Atomic, Encoded>(sel, imp, cls); return; } if (b[i].sel() == sel) { // The entry was added to the cache by some other thread // before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock. return; } } while (fastpath((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin)); cache_t::bad_cache(receiver, (SEL)sel, cls); } // 6、经过上面分析,在调用 [self studentTest]; 时,会先从 self.class 里面查找缓存,此时是没有的,因为 super 调用时缓存是在 superClass 里面的,所以这里会从新走消息发送的流程。
扯归扯,但是这里一定要清楚这里的方法查找和缓存是针对 cls 的。
关于这个很扯问题的分析使用的是 objc 最新的代码版本(781),和之前的版本是有一些不同的,关于最新版本 objc 的优化项可以看这里 。
几个 runtime 相关的应用 常用的几个类的实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 + (Class)class { return self; } - (Class)class { return object_getClass(self); } + (Class)superclass { return self->superclass; } - (Class)superclass { return [self class]->superclass; } + (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls { return self->ISA() == cls; } - (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls { return [self class] == cls; } + (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls { for (Class tcls = self->ISA(); tcls; tcls = tcls->superclass) { if (tcls == cls) return YES; } return NO; } - (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls { for (Class tcls = [self class]; tcls; tcls = tcls->superclass) { if (tcls == cls) return YES; } return NO; }
这里需要注意的有两个:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 // 1、isKindOfClass 与 isMemberOfClass 的区别 -+ (BOOL)isKindOfClass:(Class)cls; -+ (BOOL)isMemberOfClass:(Class)cls; // 2、object_getClass 与 objc_getClass 的区别 Class object_getClass(id obj) { if (obj) return obj->getIsa(); else return Nil; } Class objc_getClass(const char *aClassName) { if (!aClassName) return Nil; // NO unconnected, YES class handler return look_up_class(aClassName, NO, YES); }
经典的 hook 实现 创建两个测试类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 @interface Animal : NSObject @end @implementation Animal - (void)animalTest { NSLog(@"Animal test"); } @end @interface Person : Animal @end @implementation Person + (void)load { static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(animalTest)); Method swizzlingMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(hook_animalTest)); method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzlingMethod); }); } - (void)hook_animalTest { NSLog(@"hook_animalTest test"); [self hook_animalTest]; } @end int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { // 测试 1 Person * p = [[Person alloc] init]; [p animalTest]; // 测试 2 Animal * a = [[Animal alloc] init]; [a animalTest]; } return 0; }
如上,我们 hook animalTest方法,然后运行
测试1 可以看到如下打印:
1 2 2020-07-22 14:53 :25.496785+0800 debug-objc [75368:2985804] hook_animalTest test 2020-07-22 14:53 :25.500559+0800 debug-objc [75368:2985804] Animal test
但是到测试2 的时候程序程序挂掉了,可以看下crash信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 2020-07-22 14:54:43.493195+0800 debug-objc[75425:2989235] hook_animalTest test 2020-07-22 14:54:43.493866+0800 debug-objc[75425:2989235] Animal test 2020-07-22 14:54:45.558115+0800 debug-objc[75425:2989235] hook_animalTest test 2020-07-22 14:54:45.558828+0800 debug-objc[75425:2989235] -[Animal hook_animalTest]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x1019183a0 2020-07-22 14:54:45.563992+0800 debug-objc[75425:2989235] *** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '-[Animal hook_animalTest]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x1019183a0' *** First throw call stack: ( 0 CoreFoundation 0x00007fff374ffbe7 __exceptionPreprocess + 250 1 libobjc.A.dylib 0x000000010038f350 objc_exception_throw + 48 2 CoreFoundation 0x00007fff3757ec77 -[NSObject(NSObject) __retain_OA] + 0 3 CoreFoundation 0x00007fff3746444b ___forwarding___ + 1427 4 CoreFoundation 0x00007fff37463e28 _CF_forwarding_prep_0 + 120 5 debug-objc 0x0000000100001bfd -[Person hook_animalTest] + 61 6 debug-objc 0x0000000100001c9d main + 141 7 libdyld.dylib 0x00007fff7147ecc9 start + 1 ) libc++abi.dylib: terminating with uncaught exception of type NSException
为什么会出现这种情况呢?
来分析下 method_exchangeImplementations其实就是交换两个方法的 IMP,由于 animalTest方法是在父类 Animal 里面,所以在子类 Person 要交换方法时,其实交换的是父类 Animal 里面的方法实现,这种情况对子类Person是没有影响的,完全可以达到 hook 的目的,但是对父类 Animal 就不一样了,因为这种方法直接替换了父类的实现,当父类在调用 animalTest时其实最终就是在调用子类的 hook_animalTest,因为两个方法的IMP已经交换了,然后子类里面在执行 [self hook_animalTest]时,此时的 self 是 Animal,意思是向 Animal 发送 hook_animalTest的消息,根据我们上面分析的消息发送机制可以得到这里必然会出现这个经典的crash **unrecognized selector sent to instance。
为了解决上面的隐藏问题,我们来看下 hook 的正确姿势:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 + (void)load { static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(animalTest)); Method swizzlingMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(hook_animalTest)); // 如果返回 YES 则证明当前类没有这个方法,也就是说该方法可能在父类里面,所以需要将我们最终目标的 method 添加到 Person 里面,并且将 Person 的 hook_animalTest 方法与原来 method 互换。 // 如果返回 NO 则证明当前类有这个方法,直接交换就好 BOOL addResult = class_addMethod(self, method_getName(originalMethod), method_getImplementation(swizzlingMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzlingMethod)); if (addResult) { class_replaceMethod(self, method_getName(swizzlingMethod), method_getImplementation(originalMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod)); } else { method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzlingMethod); } }); }
来看下 objc 源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types) { if (!cls) return NO; mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock); // addMethod返回的 IMP == nil ? YES : NO return ! addMethod(cls, name, imp, types ?: "", NO); } static IMP addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types, bool replace) { IMP result = nil; runtimeLock.assertLocked(); checkIsKnownClass(cls); ASSERT(types); ASSERT(cls->isRealized()); method_t *m; // 1、如果 cls 里面有 name 对应的 method,则直接返回对应的 IMP if ((m = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, name))) { // already exists if (!replace) { result = m->imp; } else { result = _method_setImplementation(cls, m, imp); } } else { // 2、如果没有,则将 hook 的方法添加到 cls 中 method_list_t *newlist; newlist = (method_list_t *)calloc(sizeof(*newlist), 1); newlist->entsizeAndFlags = (uint32_t)sizeof(method_t) | fixed_up_method_list; newlist->count = 1; newlist->first.name = name; newlist->first.types = strdupIfMutable(types); newlist->first.imp = imp; prepareMethodLists(cls, &newlist, 1, NO, NO); cls->data()->methods.attachLists(&newlist, 1); flushCaches(cls); result = nil; } return result; }
再来看下 replace 源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 // 可以看出和 class_addMethod 源码调用的是同一个方法,只不过给 addMethod 的最后一个参数:replace 传的 YES IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types) { if (!cls) return nil; mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock); return addMethod(cls, name, imp, types ?: "", YES); } // 如果 replace 为 YES是走的 _method_setImplementation 方法 // 可以看出这里就是替换了 method_t 的 IMP static IMP _method_setImplementation(Class cls, method_t *m, IMP imp) { runtimeLock.assertLocked(); if (!m) return nil; if (!imp) return nil; IMP old = m->imp; m->imp = imp; // Cache updates are slow if cls is nil (i.e. unknown) // RR/AWZ updates are slow if cls is nil (i.e. unknown) // fixme build list of classes whose Methods are known externally? flushCaches(cls); adjustCustomFlagsForMethodChange(cls, m); return old; }
参考神经病院系列:
https://halfrost.com/objc_runtime_isa_class/ https://halfrost.com/objc_runtime_objc_msgsend/ https://halfrost.com/how_to_use_runtime/